-
€

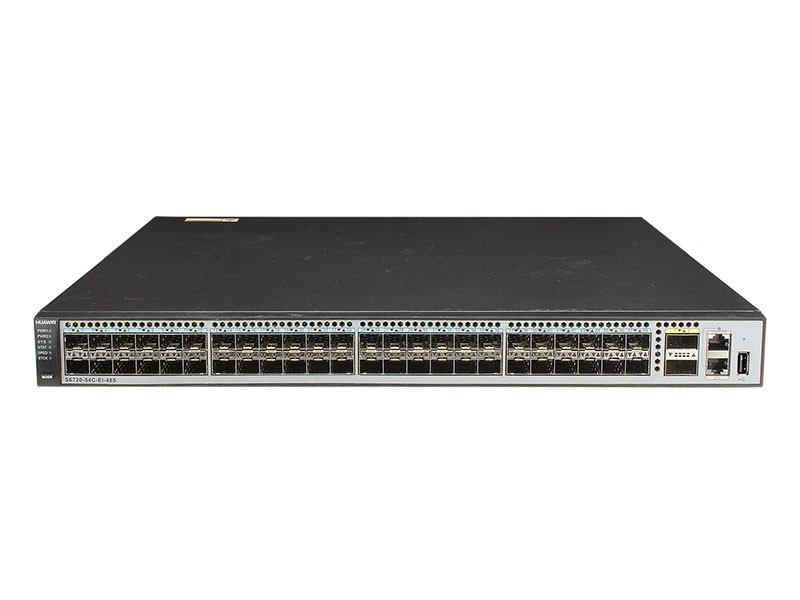
The S6720-EI series switches are next-generation 10G box switches. The S6720-EI can function as an access switch in an Internet data center (IDC) or a core/aggregation switch on a campus network.
The S6720-EI has industry-leading performance, provides line-speed 10GE access ports and line-speed 40GE uplink ports. It can be used in a data center to provide 10 Gbit/s access to servers or function as a core switch on a campus network to provide 10 Gbit/s traffic aggregation. In addition, the S6720-EI provides a wide variety of services, comprehensive security policies, and various QoS features to help customers build scalable, manageable, reliable, and secure data centers.
S6720S-26Q-EI-24S is a compact switch with 220mm depth, perfectly suitable in a 300 mm deep cabinet, saving installation space for customers.
- 48×10GE SFP+, 2×40GE QSFP+ ports
- One extended slot
- Double hot swappable AC/DC power supplies
- Forwarding performance: 1080 Mpps
- Switching capacity: 2.56 Tbps
Large-capacity, High-density, 10 Gbit/s Access and 40 Gbit/s Uplink
To provide sufficient bandwidth for users, many servers, particularly those in data centers, use 10G network adapters. The S6720-EI can be used in data centers to provide high forwarding performance and 10GE ports. The S6720-EI has the high density of all 10GE ports and the large switching capacity. Each S6720-EI provides a maximum of 6 line-speed QSFP+ ports and 48 line-speed 10GE ports.
S6720-EI ports support 1GE and 10GE access and can identify optical module types, maximizing the return on investment and allowing users to flexibly deploy services.
The S6720-EI has a large buffering capacity and uses an advanced buffer scheduling mechanism to ensure non-block transmission when data center traffic volume is high
Comprehensive Security Policies
The S6720-EI provides multiple security measures to defend against Denial of Service (DoS) attacks, as well as attacks against networks or users. DoS attack types include SYN Flood attacks, Land attacks, Smurf attacks, and ICMP Flood attacks. Attacks to networks refer to STP BPDU/root attacks. Attacks to users include bogus DHCP server attacks, man-in-the-middle attacks, IP/MAC spoofing attacks, and DHCP request flood attacks. DoS attacks that change the CHADDR field in DHCP packets are also attacks against users.
The S6720-EI supports DHCP snooping, which generates user binding entries based on users' access interfaces, MAC addresses, IP addresses, IP address leases, and VLAN IDs. DHCP snooping discards invalid packets that do not match any binding entries, such as ARP spoofing packets and IP spoofing packets. This prevents hackers from using ARP packets to initiate attacks on campus networks. The interface connected to a DHCP server can be configured as a trusted interface to protect the system against bogus DHCP server attacks.
The S6720-EI supports strict ARP learning, which prevents ARP spoofing attacks that exhaust ARP entries. The S6720-EI also provides an IP source check to prevent DoS attacks caused by MAC address spoofing, IP address spoofing, and MAC/IP spoofing. URPF, provided by the S6720-EI, authenticates packets by checking the packet transmission path in reverse, which can protect the network against source address spoofing attacks.
The S6720-EI supports centralized MAC address authentication and 802.1x authentication. The S6720-EI authenticates users based on statically or dynamically bound user information such as the user name, IP address, MAC address, VLAN ID, access interface, and flag indicating whether antivirus software is installed. VLANs, QoS policies, and ACLs can be dynamically applied to users.
The S6720-EI can limit the number of MAC addresses learned on an interface to prevent attackers from exhausting MAC address entries by using bogus source MAC addresses. This function minimizes the packet flooding that occurs when users’ MAC addresses cannot be found in the MAC address table.
This series of switches supports MACsec, a secure LAN communication method based on 802.1AE and 802.1X. The switches provide identity authentication, data encryption, integrity check, and replay protection to protect Ethernet frames and prevent attack packets.
Higher Reliability Mechanism
The S6720-EI supports redundant power supplies. You can choose a single power supply or use two power supplies to ensure device reliability. With two fans, the S6720-EI has a longer MTBF time than its counterpart switches.
The S6720-EI supports MSTP multi-process that enhances the existing STP, RSTP, and MSTP implementation. This function increases the number of MSTPs supported on a network. It also supports enhanced Ethernet reliability technologies such as Smart Link and RRPP, which implement millisecond-level protection switchover and ensure network reliability. Smart Link and RRPP both support multi-instance to implement load balancing among links, optimizing bandwidth usage.
The S6720-EI supports the enhanced trunk (E-Trunk) feature. When a CE is dual-homed to two S6720s-EI (PEs), E-Trunk protects the links between the CE and PEs and implements backup between the PEs. E-trunk enhances link reliability between devices.
The S6720-EI supports the Smart Ethernet Protection (SEP) protocol, a ring network protocol applied to the link layer on
an Ethernet network. SEP can be used on open ring networks and can be deployed on upper-layer aggregation devices to provide fast switchover (within 50 ms), ensuring the non-stop transmission of services. SEP features simplicity, high reliability, fast switchover, easy maintenance, and flexible topology, facilitating network planning and management.
The S6720-EI supports Ethernet Ring Protection Switching (ERPS), also referred to as G.8032. As the latest ring network protocol, ERPS was developed based on traditional Ethernet MAC and bridging functions and uses mature Ethernet OAM function and a ring automatic protection switching (R-APS) mechanism to implement millisecond-level protection switching. ERPS supports various services and allows flexible networking, helping customers build a network with lower OPEX and CAPEX.
The S6720-EI supports VRRP. Two S6720s-EI can form a VRRP group to ensure nonstop reliable communication. Multiple equal-cost routes to upstream devices can be configured on the S6720-EI to provide route redundancy. When an active route is unreachable, traffic is switched to a backup route.
Enhanced QoS Control Mechanism
The S6720-EI implements complex traffic classification based on packet information, such as the 5-tuple, IP preference, ToS, DSCP, IP protocol type, ICMP type, TCP source port, VLAN ID, Ethernet protocol type, and CoS. ACLs can be applied to inbound or outbound directions on an interface. The S6720-EI supports a flow-based two-rate three-color CAR. Each port supports eight priority queues, multiple queue scheduling algorithms, such as WRR, DRR, SP, WRR+SP, and DRR+SP, and WRED, a congestion avoidance algorithm. All of these features ensure high-quality voice, video, and data services.
High Scalability
The S6720-EI supports the iStack function, which allows switches that are far apart to form a stack. A port on the S6720-EI can be configured as a stack port using a command for flexible stack deployment. The distance between stacked switches is further increased when the switches are connected with optical fibers. A stack is easier to expand, is more reliable, and has a higher performance rate than a single switch. New member switches can be added to a stack without interrupting services when the system capacity needs to be increased or a member switch fails. Compared with the stacking of chassis-shaped switches, the iStack function can increase system capacity and port density without being restricted by hardware. Multiple devices in a stack can function as one logical device, which simplifies network management and configuration.
Convenient Management
The S6720-EI supports automatic configuration, plug-and-play, deployment using a USB flash drive, and batch remote upgrades. These capabilities simplify device management and maintenance and reduce maintenance costs.
The S6720-EI supports SNMP v1/v2c/v3 and provides flexible methods for managing devices. Users can manage the S6720-EI using the CLI, Web NMS and Telnet. The NQA function assists users with network planning and upgrades. In addition, the S6720-EI supports NTP, SSH v2, HWTACACS, RMON, log hosts, and port-based traffic statistics.
The S6720-EI supports GARP VLAN Registration Protocol (GVRP), which dynamically distributes, registers, and propagates VLAN attributes to reduce network administrator workloads and ensure correct VLAN configuration. In a complex network topology, GVRP simplifies VLAN configuration and reduces network communication faults caused by incorrect VLAN configuration.
The S6720-EI supports Multiplex VLAN (MUX VLAN). MUX VLAN isolates Layer 2 traffic between interfaces in a VLAN. Interfaces in a subordinate separate VLAN can communicate with ports in the principal VLAN, but cannot communicate with each other. MUX VLAN is typically used on an enterprise intranet to isolate user interfaces from each other while still allowing them to communicate with server interfaces. This function prevents communication between network devices connected to certain interfaces or interface groups, but allows these devices to communicate with the default gateway.
The S6720-EI supports BFD, which provides millisecond-level fault detection for protocols, such as OSPF, IS-IS, VRRP, and PIM, to improve network reliability. Complying with IEEE 802.3ah and 802.1ag, the S6720-EI supports point-to-point Ethernet fault management and can detect faults in the last mile of an Ethernet link to users. Ethernet OAM improves Ethernet network management and maintenance capabilities and ensures a stable network.
Various IPv6 Features
The S6720-EI supports IPv4/IPv6 dual stack and can migrate from an IPv4 network to an IPv6 network. S6720-EI hardware supports IPv4/IPv6 dual stack, IPv6 over IPv4 tunnels (including manual tunnels, 6to4 tunnels, and ISATAP tunnels), and Layer 3 line-speed forwarding. The S6720-EI can be deployed on IPv4 networks, IPv6 networks, or networks that run both IPv4 and IPv6. This makes networking flexible and enables a network to migrate from IPv4 to IPv6.
The S6720-EI supports various IPv6 routing protocols, including RIPng and OSPFv3. The S6720-EI uses the IPv6 Neighbor Discovery Protocol (NDP) to manage packets exchanged between neighbors. It also provides a path MTU (PMTU) discovery mechanism to select a proper MTU on the path from the source to the destination, optimizing network resource utilization and obtaining the maximum throughput.
Cloud-based Management
The Huawei cloud management platform allows users to configure, monitor, and inspect switches on the cloud, reducing on-site deployment and O&M manpower costs and decreasing network OPEX. Huawei switches support both cloud management and on-premise management modes. These two management modes can be flexibly switched as required to achieve smooth evolution while maximizing return on investment (ROI).
VXLAN
VXLAN is used to construct a Unified Virtual Fabric (UVF). As such, multiple service networks or tenant networks can bedeployed on the same physical network, and service and tenant networks are isolated from each other. This capability truly achieves 'one network for multiple purposes'. The resulting benefits include enabling data transmission of different services or customers, reducing the network construction costs, and improving network resource utilization. The S6720-EI series switches are VXLAN-capable and allow centralized and distributed VXLAN gateway deployment modes. These switches also support the BGP EVPN protocol for dynamically establishing VXLAN tunnels and can be configured using NETCONF/YANG.
OPS
Open Programmability System (OPS) is an open programmable system based on the Python language. IT administrators can program the O&M functions of a switch through Python scripts to quickly innovate functions and implement intelligent O&M.
Intelligent O&M
The S6720-EI provides telemetry technology to collect device data in real time and send the data to Huawei campus network analyzer CampusInsight. The CampusInsight analyzes network data based on the intelligent fault identification algorithm, accurately displays the real-time network status, effectively demarcates and locates faults in a timely manner, and identifies network problems that affect user experience, accurately guaranteeing user experience.
The S6720-EI supports a variety of intelligent O&M features for audio and video services, including the enhanced Media Delivery Index (eMDI). With this eDMI function, the S6720-EI can function as a monitored node to periodically conduct statistics and report audio and video service indicators to the CampusInsight platform. In this way, the CampusInsight platform can quickly demarcate audio and video service quality faults based on the results of multiple monitored nodes.
Intelligent Upgrade
Switches support the intelligent upgrade feature. Specifically, switches obtain the version upgrade path and download the
newest version for upgrade from the Huawei Online Upgrade Platform (HOUP). The entire upgrade process is highly automated and achieves one-click upgrade. In addition, preloading the version is supported, which greatly shortens the upgrade time and service interruption time.
The intelligent upgrade feature greatly simplifies device upgrade operations and makes it possible for the customer to upgrade the version independently. This greatly reduces the customer's maintenance costs. In addition, the upgrade policies on the HOUP platform standardize the upgrade operations, which greatly reduces the risk of upgrade failures.
Specification:
|
S6720-54C-EI-48S-AC |
|
| Fixed Port |
48 ×10GE SFP+ 2×40GE QSFP+ ports |
| Extended slot | One extended slot for 4× 40 GE QSFP+ and 8 x 10 GE SFP+ interface card |
|
MAC address table |
288k MAC address entries MAC address learning and aging Static, dynamic, and black hole MAC address entries Packet filtering based on source MAC addresses |
| VLAN | 4K VLANs Guest VLAN and voice VLAN VLAN assignment based on MAC addresses, protocols, IP subnets, policies, and ports 1:1 and N:1 VLAN Mapping QinQ and selective QinQ |
|
IPv4 routing |
Static routing, RIPv1, RIPv2, ECMP, and URPF OSPF, IS-IS, and BGP VRRP Policy-based routing Routing policy |
|
IPv6 routing |
Static route RIPng OSPFv3 BGP4+ ISISv6 |
| IPv6 features | Neighbor Discovery (ND) PMTU IPv6 ping, IPv6 tracert, and IPv6 Telnet 6to4 tunnel, ISATAP tunnel, and manually configured tunnel ACLs based on the source IPv6 address, destination IPv6 address, Layer 4 ports, or protocol type MLD v1/v2 snooping |
| Multicast |
Static Layer 2 multicast MAC address MSDP |
|
QoS/ACL |
Rate limiting on packets sent and received by an interface Packet redirection Port-based traffic policing and two-rate three-color CAR Eight queues on each port WRR, DRR, SP, WRR+SP, and DRR+SP queue scheduling algorithms Re-marking of the 802.1p priority and DSCP priority Packet filtering at Layer 2 to Layer 4, filtering out invalid frames based on the source MAC address, destination MAC address, source IP address, destination IP address, port number, protocol type, and VLAN ID Rate limiting in each queue and traffic shaping on ports |
| MPLS | MPLS, MPLS VLL, L3VPN |
| VPLS | Martini VPLS |
| Reliability | STP (IEEE 802.1d), RSTP (IEEE 802.1w), and MSTP (IEEE 802.1s) BPDU protection, root protection, and loop protection RRPP ring topology and RRPP multi-instance Smart Link tree topology and Smart Link multi-instance, providing the millisecond-level protection switchover SEP ERPS (G.8032 v2) BFD for OSPF, BFD for IS-IS, BFD for VRRP, and BFD for PIM E-Trunk |
| Security | User privilege management and password protection DoS attack defense, ARP attack defense, and ICMP attack defense Binding of the IP address, MAC address, interface, and VLAN Port isolation, port security, and sticky MAC Blackhole MAC address entries Limit on the number of learned MAC addresses 802.1x authentication and limit on the number of users on an interface AAA authentication, RADIUS authentication and TACACS authentication SSH v2.0 Hypertext Transfer Protocol Secure (HTTPS) CPU defense Blacklist and whitelist MACSec |
| Super Virtual Fabric (SVF) | Working as the parent node to vertically virtualize downlink switches as one device for management? supports two-layer clients architecture Support as a client node to be managed by SVF parent |
| VXLAN | Supports the VXLAN function. Configured through the NETCONF protocol. |
| Management and maintenance |
iStack (using service ports as stack ports) MAC Forced Forwarding (MFF) |
| Operating environmen |
Operating temperature: 0-1800 m: 0-45?; 1800-5000 m: decrease 1? when the altitude increases every 220 m
Relative humidity: 5% to 95% (non-condensing) |
|
Input voltage |
Rated voltage range: 100 V to 240 V AC, 50/60 Hz |
| Dimensions (W x D x H, mm) | 442 x 420 x 44,4 |
| Height | 1U |
| Typical power consumption |
without subcard: 190W |




 Polski
Polski English
English Italiano
Italiano Español
Español Čeština
Čeština Српски
Српски Deutsch
Deutsch Ελληνικά
Ελληνικά Slovenský
Slovenský





