-
€










Huawei AP661 è un punto di accesso della serie eKitEngine che supporta lo standard Wi-Fi 6. Supporta i protocolli IEEE 802.11 b/g/n/ax nella banda da 2,4 GHz e IEEE 802.11 a/n/ac nella banda da 5 GHz. Nella banda da 2,4 GHz gestisce una trasmissione 2x2 MIMO, mentre nella banda da 5 GHz supporta due trasmissioni: 2x2 MIMO e 4x4 MIMO. La velocità di trasmissione massima teorica combinata è di 6600 Mb/s.
Il dispositivo supporta la tecnologia MU-MIMO (trasmissione e ricezione simultanea di dati da più utenti) e il BSS Coloring (etichettatura delle trasmissioni per ridurre le interferenze). Il punto di accesso è dotato di un'antenna di tipo Smart, la cui struttura è composta da più elementi che possono operare indipendentemente. Gli elementi dell'antenna possono modificare la forma del fascio principale in base alle necessità, adattandosi ai dispositivi connessi.
L'AP661 è progettato per ambienti con un elevato numero di utenti e può gestire numerosi dispositivi client connessi senza ridurre le prestazioni della rete. L'involucro è adatto per il montaggio a parete, a soffitto o su una guida con scanalatura a T.
Il dispositivo è dotato di una porta Ethernet 2.5G (10/100/1000/2500 Mb/s) e di una porta Ethernet gigabit (10/100/1000 Mb/s). L'alimentazione può essere fornita tramite PoE conforme allo standard 802.3at o tramite un connettore DC (12 V).
Il prodotto offerto può operare in diversi modi: Fat AP, Leader AP, Fit AP o Cloud. In modalità Fat AP, il dispositivo funziona in modo indipendente e può essere configurato come un normale router wireless. La modalità Leader AP consente di configurare l’AP661 come dispositivo master (leader), che gestisce altri punti di accesso compatibili. La modalità Cloud permette di collegare il dispositivo a un controller basato su cloud, mentre la modalità Fit AP serve per il collegamento con un controller WLAN AC fisico. Le soluzioni della serie eKitEngine consentono di creare una rete wireless estesa ed efficiente, in grado di coprire ampie superfici. I dispositivi supportano il roaming dei dati, il controllo della banda e diverse metodologie di autenticazione. L’AP661 è ideale per ambienti con un elevato numero di utenti, come sale conferenze, concerti o padiglioni fieristici.
Rete Wi-Fi 6 AX6600, Bluetooth
L’AP661 è progettato per trasmettere una rete wireless Wi-Fi 6 e supporta i protocolli IEEE 802.11 b/g/n/ax nella banda da 2,4 GHz e IEEE 802.11 a/n/ac/ax nella banda da 5 GHz. Il dispositivo può gestire simultaneamente tre trasmissioni radio: 2,4 GHz 2x2 MIMO, 5 GHz 2x2 MIMO e 5 GHz 4x4 MIMO (2 + 2 + 4). Grazie a questa configurazione, la velocità massima teorica è di 574 Mb/s a 2,4 GHz, 1201 Mb/s a 5 GHz con 2x2 MIMO e 4804 Mb/s a 5 GHz con 4x4 MIMO.
Queste elevate prestazioni sono particolarmente adatte per ambienti destinati a numerosi utenti simultanei. L'AP661 garantisce un’adeguata larghezza di banda in situazioni in cui i punti di accesso standard non sarebbero in grado di fornire velocità di trasmissione sufficienti ai dispositivi client.
Il punto di accesso sfrutta anche numerose funzionalità aggiuntive che migliorano la qualità della rete. MU-MIMO consente di trasmettere e ricevere dati simultaneamente da più client, eliminando il fenomeno dell’accodamento dei dati. Beamforming ottimizza la direzione del segnale per migliorare la connessione con i dispositivi situati ai margini della copertura, mentre TWT (Target Wake Time) aiuta a risparmiare energia attivando i dispositivi connessi solo quando è necessaria una trasmissione di dati.
Inoltre, il dispositivo supporta la trasmissione Bluetooth (BLE 5.2), che può essere utilizzata per la gestione remota, la localizzazione o applicazioni IoT.
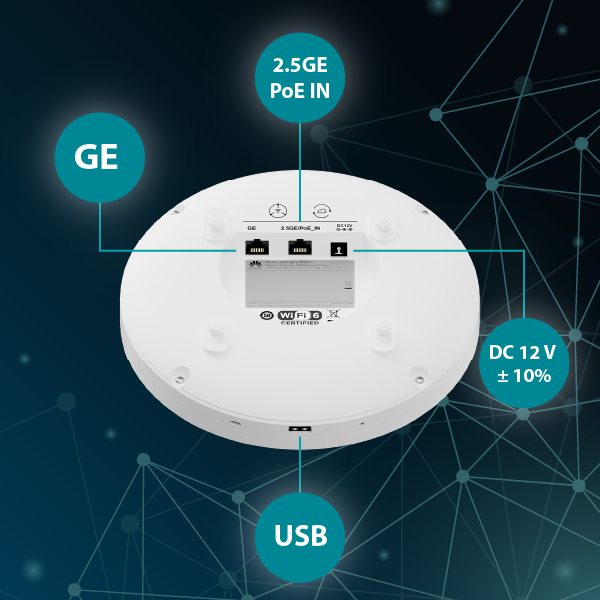


Port 2.5G Ethernet, port 1G Ethernet, porta USB, alimentazione PoE e connettore DC
Il prodotto offerto è dotato di un port 2.5G Ethernet (10/100/1000/2500 Mb/s) e un port Gigabit Ethernet (10/100/1000 Mb/s). Il port 2.5G funge anche da ingresso per l’alimentazione PoE conforme allo standard IEEE 802.3at, mentre l’alimentazione può essere fornita anche tramite un connettore DC standard (12 V). Il consumo energetico massimo, escludendo l’USB, è di 21,2 W.
Il produttore ha integrato una porta USB pensata per il collegamento di un modem esterno per applicazioni IoT, come ZigBee o RFID.
Antenne Smart
Punkt dostępowy posiada anteny typu Smart, konstrukcja anteny składa się z wielu elementów, które mogą pracować niezależnie od siebie. Elementy anteny w zależności od potrzeb mogą modyfikować kształt wiązki głównej tak, aby doprowadzić do podłączonych klientów jak najlepszy zasięg. Urządzenie dopasowuje się do warunków radiowych i zapewnia znacznie lepsze pokrycie sygnałem od AP wyposażonych w zwykłe anteny dookólne. Zysk energetyczny wynosi 4 dBi w paśmie 2,4 GHz i 5 dBi w 5 GHz.


Fino a 1536 clienti
Il Huawei AP661 può gestire fino a 1536 client simultanei (512 per radio) ed è stato progettato per ambienti estremamente impegnativi, come padiglioni fieristici e aree concerti. Il produttore consiglia di limitare il numero di client attivi a un massimo di 300, garantendo così una larghezza di banda di circa 22 Mb/s per ogni dispositivo, più che sufficiente per un utilizzo standard di internet. Il sistema supporta il bilanciamento del carico e il smart roaming, permettendo di spostare automaticamente gli utenti su un altro punto di accesso in caso di sovraccarico.
L’algoritmo DFA rileva automaticamente la congestione dei canali wireless e riconosce eventuali interferenze tra trasmissioni sovrapposte. Quando vengono utilizzati più punti di accesso, questi operano in modo coordinato per evitare interferenze reciproche. Inoltre, le tecnologie EDCA e airtime scheduling consentono di pianificare l’uso del canale per ciascun dispositivo client, garantendo un accesso equo alla rete.
Un ulteriore vantaggio della serie AP eKitEngine è l’ottimizzazione dell’utilizzo della rete da parte dei dispositivi client. I client con segnale troppo debole o connessione lenta vengono automaticamente disconnessi per migliorare la qualità complessiva della trasmissione. L’AP661 è dotato della funzione 5G-prior, che privilegia le connessioni nella banda da 5 GHz, garantendo la massima larghezza di banda possibile e riducendo significativamente il carico e le interferenze nella banda da 2,4 GHz.
Sistema wireless avanzato
Il prodotto offerto è progettato per funzionare all'interno di un sistema wireless su larga scala, composto da più punti di accesso. Questa rete può coprire aree molto estese, a seconda del numero di dispositivi utilizzati. Il sistema supporta il roaming dei dati, consentendo agli utenti di essere automaticamente trasferiti tra i punti di accesso senza perdere la connessione.
Le soluzioni Huawei offrono un'ampia gamma di funzionalità avanzate per il controllo della larghezza di banda, il miglioramento della qualità della trasmissione e la sicurezza. Per l’autenticazione degli utenti, è possibile utilizzare protocolli come 802.1x, autenticazione basata su indirizzo MAC o captive portal.
Il sistema di gestione e monitoraggio avanzato consente di ridurre il tempo di amministrazione della rete, grazie a funzionalità come il rilevamento automatico e la diagnosi di errori, migliorando così l’efficienza operativa.


Quattro modalità di funzionamento
Il punto di accesso può operare in quattro modalità:
Fat AP – Il punto di accesso funziona in modo autonomo, con una configurazione e una gestione simili a quelle di un router wireless standard. È ideale per piccole reti che richiedono l’uso di un solo AP.
Leader AP – Permette di configurare il dispositivo come "leader", assumendo il ruolo di controller nella rete. In questa modalità, è possibile collegare altri punti di accesso per creare un sistema più ampio. Questa soluzione è particolarmente adatta a piccole reti, come uffici o ristoranti, riducendo i costi di acquisto di un controller separato.
Cloud AP – Consente la gestione del punto di accesso tramite una piattaforma cloud. Questo approccio semplifica il monitoraggio delle prestazioni e la configurazione remota, senza la necessità di dispositivi di gestione aggiuntivi.
Fit AP – È la modalità predefinita in cui il punto di accesso si collega direttamente a un controller di rete.
Numerose applicazioni
Il Huawei AP661 trova applicazione in numerosi scenari, soprattutto in ambienti con un'elevata densità di utenti, come sale da concerto, padiglioni fieristici o grandi spazi pubblici. Grazie alla sua elevata capacità di trasmissione, garantisce connessioni stabili e veloci anche con molti dispositivi connessi simultaneamente. Dotato di funzionalità avanzate, è progettato per operare in condizioni difficili, dove altri punti di accesso potrebbero non offrire prestazioni adeguate..

Specifiche
| Huawei AP661 | |
| Caratteristiche generali | |
|---|---|
| Tipo montaggio |
Parete Sofitto Su guida con scanalatura a T |
| Dimensioni | Φ 220 mm x 50 mm |
| Peso | 1,08 kg |
| Porte Ethernet |
1 porta 2.5G Ethernet 10/100/1000/2500 Mb/s
1 porta 1G Ethernet 10/100/1000 Mb/s
1 porta USB |
| Bluetooth | BLE 5.2 |
| Diode LED | Dioda wskazuje na włączenie zasilania, włączanie urządzenia, urządzenie włączone, alarm oraz błędy systemu |
| Caratteristiche di alimentazione | |
|
Ingresso di alimentazione |
Connettore DC: 12 V ± 10% PoE: standard IEEE 802.3 at |
| Consumo massimo di energia | 21,2 W (escluso USB) |
| Caratteristiche ambientali | |
| Temperatura operativa | Da -10 a 50 °C |
| Temperatura di conservazione | Da -40 a 70 °C |
| Umidità relativa | 5%-95% senza condensazione |
|
Grado di protezione |
IP41 |
| Caratteristiche radio | |
| Tipo antenna | Antenne Smart integrate |
|
Guadagno dell'antenna |
2,4 GHz: 4 dBi 5 GHz: 5 dBi |
| Numero massimo di SSID per radio | ≤ 16 |
| Numero massimo di client | ≤ 1536 (512/radio) |
| Potenza di trasmissione massima |
2,4 GHz: 25 dBm 5 GHz (2x2 MIMO): 23 dBm 5 GHz (4x4 MIMO): 26 dBm BLE: < 10 dBm (dipende dalle normative locali) |
| Regolazione della potenza | Dokładność do 1 dBm |
| Numero massimo di canali non sovrapposti |
2.4 GHz (2.412 GHz - 2.472 GHz) 802.11 b/g
802.11 n
802.11 ax
5 GHz (5.18 GHz - 5.825 GHz) 802.11 a
802.11 n
802.11 ac
802.11 ax
|
| Modalita' Fat/Fit AP | |
| Proprieta' WLAN |
Standard IEEE 802.11 b/g/n/ax (2,4 GHz) / IEEE 802.11 a/n/ac/ax (5 GHz) MRC (Maximum Ratio Combining) STBS (Space Time Block Code) CDD (Cyclic Delay Diversity) / CSD (Cyclic Shift Diversity) Beamforming (formazione del fascio) MU-MIMO (Multi-user multiple-input multiple-output) OFDMA (Orthogonal frequency division multiple access) Modulacja do 1024QAM, wspiera także 256QAM, 64QAM, 16QAM, 8QAM, QPSK i BPSK TWT (Target wake time) LDPC (Low-density parity-check) Frame aggregation, w tym A-MPDU (Tx/Rx) oraz A-MSDU (Tx/Rx) 802.11 DFS (dynamic frequency selection) GI (Short guard interval) w trybach 20, 40, 80 i 160 MHz Mappatura e pianificazione delle priorità secondo WMM (Wi-Fi Multimedia) Gestione dei canali WLAN Scansione automatica dei canali ed evitamento delle interferenze Nascosti SSID SST (Signal sustain technology) U-APSD (Unscheduled automatic power save delivery) Supporto CAPWAP nella modalita' Fit AP (Control and Provisioning of Wireless Access Points)Login automatico in modalità Fit AP ESS in modalita' Fit AP (Extended Service Set) ACC (Advanced cellular coexistence) per minimizzare le interferenze Multi-user CAC (call admission control) Smart roaming 802.11k / 802.11r Fast roaming 802.11r (≤ 50 ms) |
| Caratteristiche di rete |
|
| Funzione QoS |
|
| Sicurezza |
Autenticazione open system Crittografia/autenticazione WEP con chiave a 64, 128, 152 o 192 bit WPA2-PSK (WPA2-Personal) WPA2-802.1X (WPA2-Enterprise) WPA3-SAE (WPA3-Personal) WPA3-802.1X (WPA3-Enterprise) Autenticazione ibrida WPA-WPA2 e WPA2-WPA3 WPA2-PPSK in modalità Fit AP WAPI WIDS (Wireless Intrusion Detection System) e WIPS (Wireless Intrusion Prevention System), inclusa la rilevazione di dispositivi rogue, attacchi, blacklist dinamica e whitelist di client/AP Autenticazione 802.1X, MAC, Portal DHCP Snooping DAI (Dynamic ARP Inspection) IPSG (IP Source Guard) 802.11w PMF (Protected Management Frames) Crittografia hardware IPsec e DTLS |
| Monitoraggio delle prestazioni |
|
|
Localizzazione |
|
| BYOD |
|
|
Analisi dello spettro |
|
| Modalita' Cloud | |
| Proprieta' WLAN |
Standardy IEEE 802.11 b/g/n/ax (2,4 GHz) / IEEE 802.11 a/n/ac/ax (5 GHz) MRC (Maximum Ratio Combining) STBS (Space Time Block Code) CDD (Cyclic Delay Diversity) / CSD (Cyclic Shift Diversity) Beamforming (kształtowanie wiązki) MU-MIMO (Multi-user multiple-input multiple-output) OFDMA (Orthogonal frequency division multiple access) Modulacja do 1024QAM, wspiera także 256QAM, 64QAM, 16QAM, 8QAM, QPSK i BPSK TWT (Target wake time) LDPC (Low-density parity-check) Frame aggregation, w tym A-MPDU (Tx/Rx) oraz A-MSDU (Tx/Rx) 802.11 DFS (dynamic frequency selection) GI (Short guard interval) w trybach 20, 40, 80 i 160 MHz Mapowanie i harmonogram priorytetów zgodnie z WMM (Wi-Fi multimedia) Zarządzanie kanałami WLAN Automatyczne skanowanie kanałów i unikanie zakłóceń Ukrywanie SSID SST (Signal sustain technology) U-APSD (Unscheduled automatic power save delivery) Automatyczne logowanie AP 802.11 k i 802.1 v smart roaming 802.11 r fast roaming (≤ 50 ms) ACC (Advanced cellular coexistence),minimalizowanie wpływu zakłóceń z sieci komórkowych |
|
Caratteristiche di rete |
|
| Funzioni QoS |
|
| Sicurezza |
|
|
Monitoraggio delle prestazioni |
|




 Polski
Polski English
English Italiano
Italiano Español
Español Čeština
Čeština Српски
Српски Deutsch
Deutsch Ελληνικά
Ελληνικά Slovenský
Slovenský




